Lupus (Lupus Erythematosus)
This page provides everything you need to know about lupus.
What is Lupus?
- Lupus is a chronic disease that affects the immune system, which defends the body against diseases and infections by attacking the body’s tissues, causing inflammation in body parts such as the joints, skin, kidneys, and heart, among others. There are types of lupus:
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): This is the most common type, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe, affecting many parts of the body.
- Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (Discoid): This type of lupus affects the skin, presenting as a rash.
-
- Drug-Induced Lupus: Caused by certain medications such as:
- Isoniazid is used to treat tuberculosis.
- Procainamide is used to regulate heartbeats.
Hydralazine is used for high blood pressure.
- Symptoms may disappear within six months after stopping the medication.
Neonatal Lupus: This type is very rare and may occur in newborns due to transmission from a mother with lupus to the fetus.
What are the Symptoms of Lupus?
- Symptoms and their severity vary from person to person and over time. Symptoms of lupus include:
- Joint pain and swelling.
- Extreme fatigue and exhaustion.
- Fever.
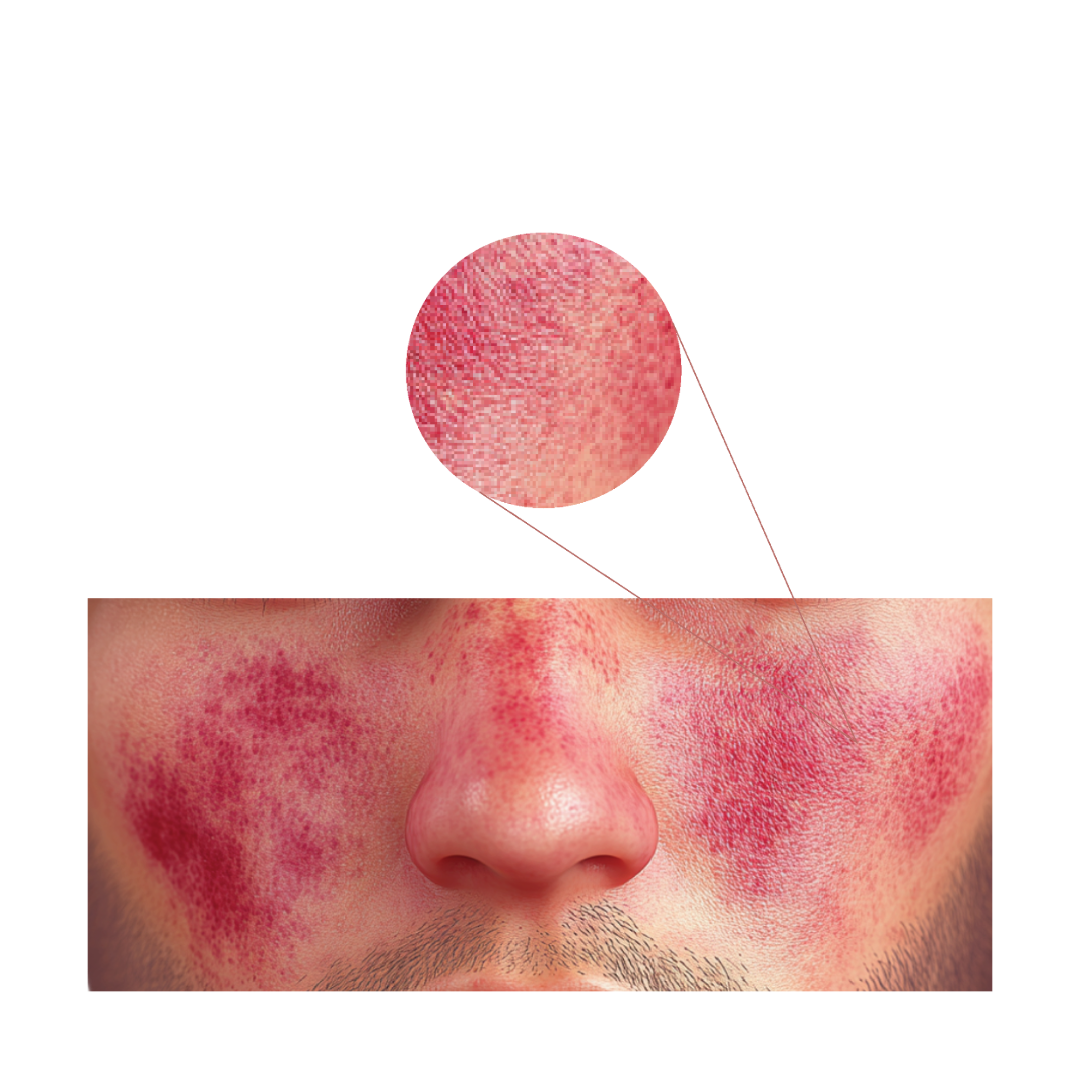
- Facial rash (butterfly-shaped) or other body areas.
- Sensitivity to sunlight.
- Dryeyes..
- Headaches andfrequent forgetfulness.
- Sores in the mouth and nose.
Kidney issues.
What are the Causes of Lupus?
- There is no clear reason why the immune system attacks body tissues, but there are risk factors that increase the chance of developing lupus, including:
- Environmental factors:
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays.
- Exposure to chemicals.
- Some medications, such as hypertension drugs, anti-seizure medications, and antibiotics.
- Exposure to viruses and infections.
- Stress.
- Age and gender, with women more commonly affected than men, often between the ages of 15 and 44.
Hormonal factors, as researchers have noted a link between increased estrogen levels and lupus, especially in women.
What are the Diagnostic Methods?:
- There is no specific test for lupus due to the variation in symptoms, but doctors take medical history and conduct clinical examinations and may request additional procedures as needed, such as:
- Laboratory tests including:
- Kidney function tests.
- Blood cell and platelet count tests.
- Antibody tests.
- X-rays.
Kidney biopsy.
What are the Treatment Methods for Lupus?
- There is no definitive treatment for lupus, but symptoms can be managed, and medications can help control them, such as:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Immunosuppressive medication.
- Corticosteroids.
Pain relievers.
How Can Lupus Be Prevented?
- There are no specific prevention methods, but there are general guidelines for individuals with lupus:
- Use sunscreen and wear a hat when going out in the sun.
- Avoid stress triggers.
- Quitsmoking.
- Exercise regularly. For more details, read the guide: “Move for You and Life.”
Follow a healthy, balanced diet.
What are the Complications of Lupus?
- If the prescribed medication is not adhered to, some complications can lead to health problems such as:
- Kidney issues.
- Anemia.
- Inflammation of theheart muscle andheart membrane.
- Breathing difficulties, lungproblems, pneumonia, andinternal lung bleeding.
- Increased risk of miscarriage during pregnancy.
Memory issues.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you experience symptoms of lupus.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can a woman with lupus get pregnant?
Yes, especially if the disease is stable with adherence to medication for at least six months to avoid miscarriage. It is important to consult a doctor when planning for pregnancy.
Is lupus contagious?