Scabies
On this page, you will find everything you need to know about scabies.
What Is Scabies?
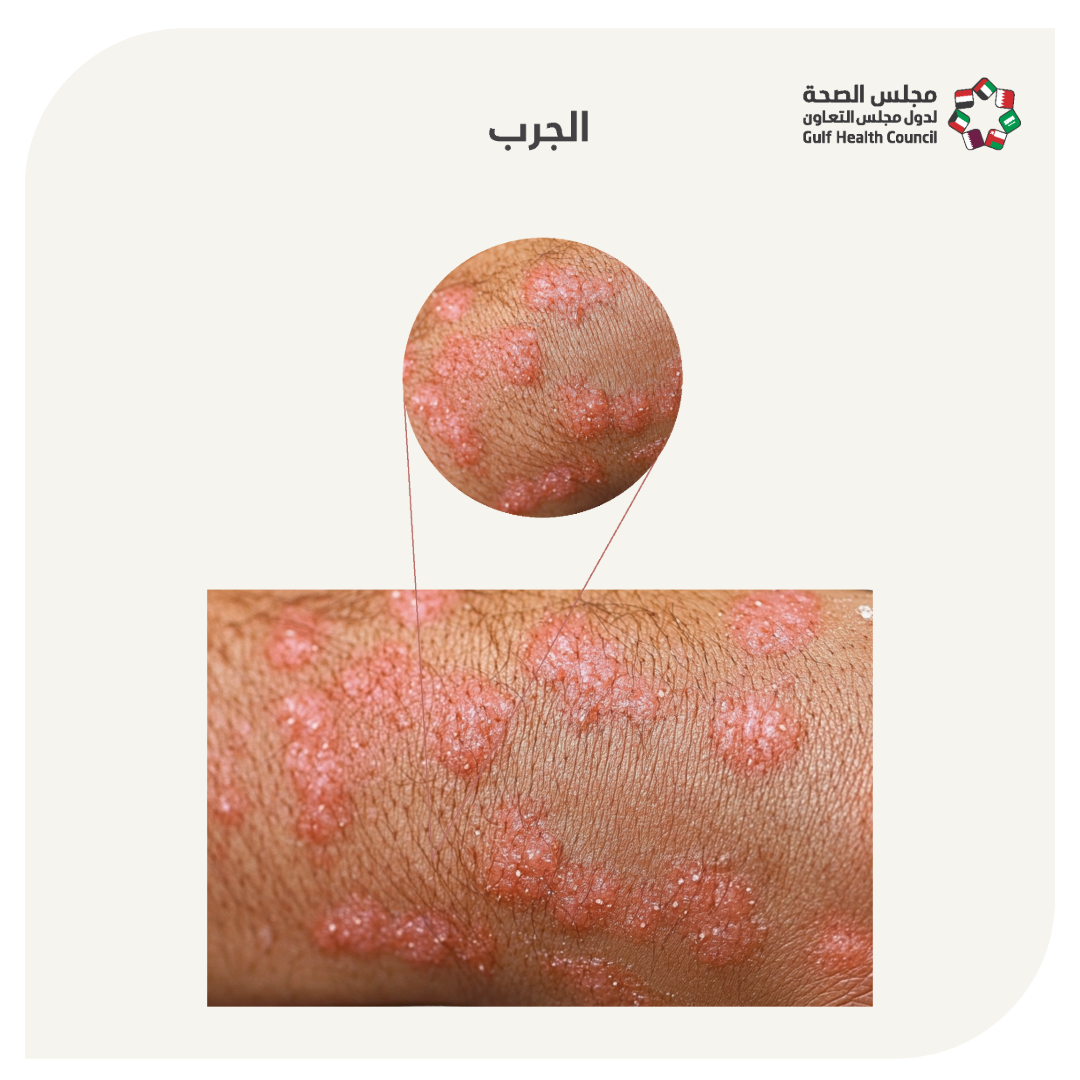
- Scabies is a skin disease caused by an infestation of the human itch mites. These mites burrow into the top layer of the skin to live and lay their eggs, which results in small red bumps and intense itching. There are different types of scabies:
- Crusted (Norwegian) Scabies: Often occurs in people with weakened immune systems and tends to form scaly areas that cover large areas of skin.
- Nodular Scabies: This type may cause brown and red nodules that remain long after scabies has disappeared, commonly occurring in children.
- Bullous Scabies: Involves the appearance of skin blisters and primarily affects adults.
Scalp Scabies: Affects the scalp and may show no symptoms other than scales resembling psoriasis.
What Are the Symptoms of Scabies?
- Scabies can infect a person for four to six weeks before early symptoms appear, with the rash spreading gradually over weeks, sometimes months. The main symptoms include:
- Intense itching, which is the most common symptom of scabies, particularly at night, leading to difficulty sleeping.
- A rash forming gray or skin-colored lines.
- Small blisters and scales.
Rash causing skin ulcers and itching due to bacteria.
- What Causes Scabies?
- A person contracts scabies when exposed to scabies mites or through the transfer of mites from an infected person through direct or indirect contact, such as using their personal items.
How Is Scabies Diagnosed?
- The doctor takes a medical history and conducts a physical examination. They may also perform additional procedures as necessary, such as:
Confirming the diagnosis by taking a skin biopsy with a thin needle to examine it under a microscope for mites or their eggs.
How Is Scabies Treated?
Treatment involves several procedures, or as required by the situation, which may include the following:
- – Medications:
Your healthcare provider should prescribe a cream containing medication to treat scabies. The cream is applied over your entire body, including the hands and soles of the feet.
- How Can Scabies be Prevented?
- Avoid direct skin contact with an infected person.
- If a family member is infected, it’s essential to treat all family members.
- Limit close contact with others if you know you have scabies.
Maintain personal hygiene and the cleanliness of bed linens and clothing.
- What Are the Complications of Scabies?
- Scabies can sometimes lead to secondary skin infections if the skin becomes irritated from scratching.
Crusted (Norwegian) scabies is a rare and more severe form that can affect all parts of the body, including the head, neck, and nails.
When Should You See a Doctor?
- Consult a doctor if you are experiencing intense itching or a persistent skin rash, or in the following situations:
- After being treated for scabies but still suffering from symptoms and skin issues after a month.
- Signs of bacterial infection appear, such as redness or sores with pus.
Side effects from medications appear.
- Frequently Asked Questions
Where do scabies mites live on the body?
-
- The mites live in tight creases and cracks of the skin, such as:
- Between the fingers and toes.
- The folds of the groin and genital area.
- Around the wrists and knees.
- The area surrounding the waist.
- Under the nails.
- Beneath rings or bracelets.
- Around the nipples.
When can a person with scabies resume normal activities?
- Infected individuals can resume normal activities 24 hours after using the first dose of the topical treatment for the first time, as the medication works quickly to kill scabies mites. It is not necessary to wait for the second dose of topical treatment, typically administered a week after the first.
Can itching continue after recovery? When might it stop?