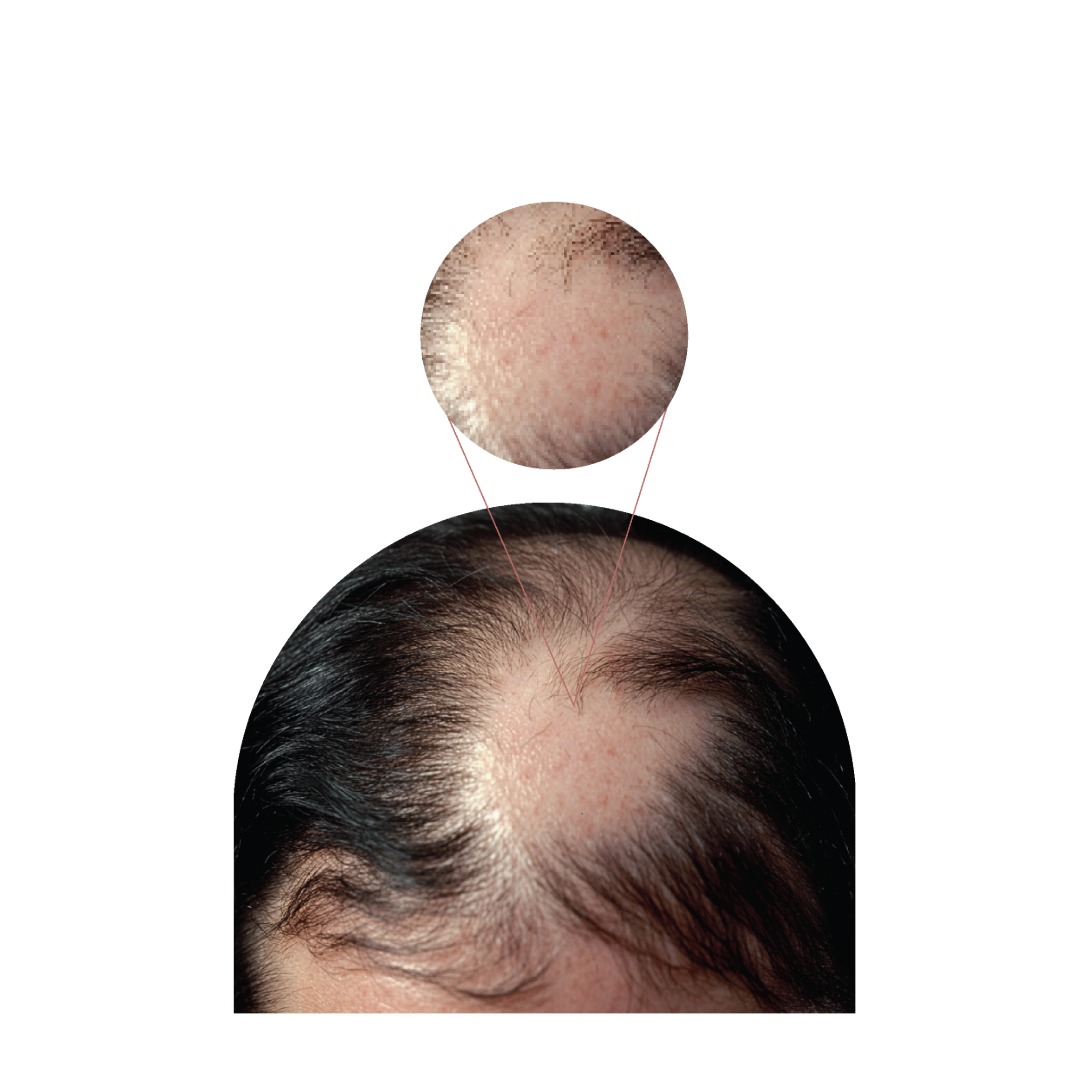
Alopecia Areata
(Diseases)
On this page, you will find everything you need to know about Alopecia Areata.
What is Alopecia Areata?
- Alopecia Areata is a non-contagious autoimmune disease that causes hair loss in one or several areas of the scalp. It does not leave scars or marks It may develop during childhood or later in life.
- There are several types of Alopecia Areata, including:
- • Alopecia Areata (patchy): Hair falls out in small round or oval patches on the scalp.
• Alopecia Totalis: Complete loss of all hair on the scalp.
• Alopecia Universalis: Complete loss of hair across the entire body.
- What are the symptoms of Alopecia Areata?
- The first signs are usually patches of hair loss on the scalp, but it can also affect the eyebrows, beard, arms, or legs. Common symptoms include:
• Round or oval bald patches.
• Smooth, hairless skin on the affected area.
What causes Alopecia Areata?
The exact cause is still unknown. Alopecia Areata occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
- How is Alopecia Areata diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. The doctor may also request:
• Laboratory tests.
- • A scalp biopsy if necessary.
- How is Alopecia Areata treated?
Treatment depends on the individual case and may include:
• Corticosteroid injections
- • Topical sprays or cream.
- How can you prevent Alopecia Areata?
- There is no known way to prevent Alopecia Areata, but some general health guidelines:
• Avoid chemical treatments on hair.
• Maintain ahealthy and balanced diet..
• Protect the scalp from sunlight by wearing hats or scarves.
What are the complications of Alopecia Areata?
Individuals with Alopecia Areata may experience psychological effects such as stress, anxiety, and depression due to changes in appearance.
When should you see a doctor?
Consult a doctor if you notice sudden or patchy hair loss, as this may require medical and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How can hair growth be stimulated?