Psoriasis
Everything You Need to Know About Psoriasis
What Is Psoriasis?
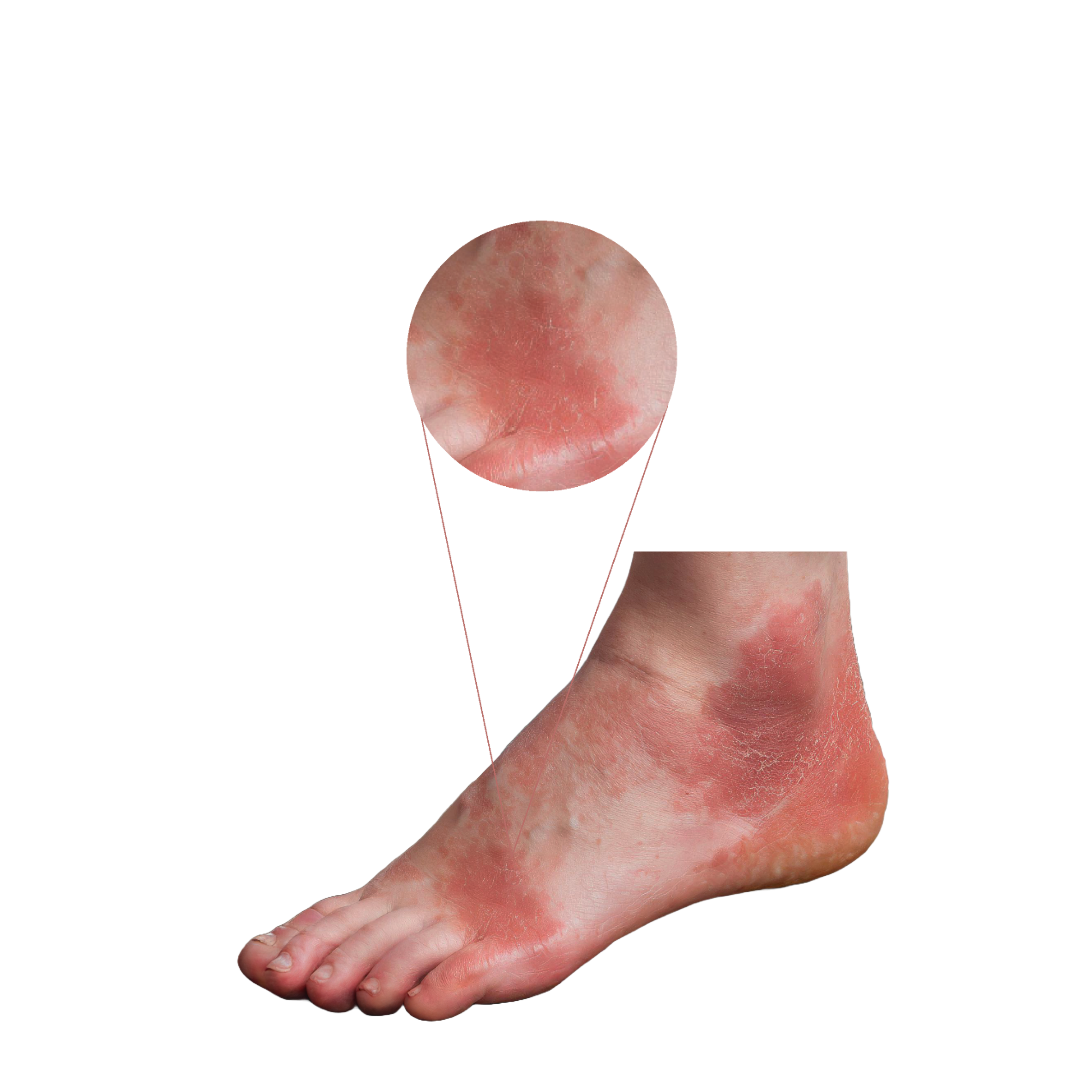
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin and nails, characterized by painful irritation, dark patches, and white or silver scales.
- Types of Psoriasis Include:Psoriastc Plaque):
Plaque Psoriasis:
- This is the most common type and is characterized by thick patches with dry scales, usually white or silver, or gray, that cover the skin.Psoriatic Arthritis):
Psoriatic Arthritis:
- This chronic form occurs when psoriasis affects the joints and is considered a complication of psoriasis. It happens when psoriasis is severe after some time has passed.Guttate Psoriasis):
Guttate Psoriasis:
- This type often affects children or young adults. It is not chronic, but in most cases, guttate psoriasis disappears within a few weeks or months without specific treatment. However, guttate psoriasis can become chronic or disappear temporarily and then reappear later.Inverse Psoriasis):
Inverse Psoriasis:
- This type of psoriasis occurs in the folds of the skin, such as under the arms and around the genital area.Pustular psoriasis)
Pustular Psoriasis:
This type features blisters filled with pus on the affected area, often on the hands or feet, and can make activities such as writing or walking unbearable.Generalized Pustular Psoriasis):
Generalized Pustular Psoriasis:
- This type is rare and serious, requiring medical care, as pustular psoriasis spreads over a large area of the skin.Erythrodermic Psoriasis):
Erythrodermic Psoriasis:
This is a rare, serious form that requires urgent healthcare. It often appears in individuals with another type of psoriasis or when the body does not respond to treatment.
Nail Psoriasis:Nail Psoriasis):
This type of psoriasis affects the nails.
What Are the Symptoms of Psoriasis?
Symptoms and signs of psoriasis vary based on the type and can either be scattered or cover large areas. Generally, symptoms of psoriasis include:
- Painful skin irritation.
- Thick, dry patches covered with white, silver, or gray scales.
- Red or dark patches on the skin.
- Burning or stinging sensation on the skin.
Psoriasis may occur anywhere on the body, but is most commonly found on:
- Elbows and knees.
- Lower back.
- Scalp.
What Causes Psoriasis?
Psoriasis occurs when there is an immune system malfunction that accelerates the growth of skin cells over days instead of weeks, causing these cells to accumulate on the skin surface and produce various symptoms.
The main reason for immune system dysfunction is unclear, but risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing psoriasis include:
- Family history of psoriasis and genetic predisposition.
- Age, typically between 20 and 30, but it can also occur later in life.
- People with white or fair skin.
How Is Psoriasis Diagnosed?
Doctors take into account the medical and family history of psoriasis and conduct a clinical examination. Additional procedures may be requested as necessary, such as::
- Skin biopsy.
What Are the Treatments for Psoriasis?
Treatment depends on various factors, including the extent and location of the affected areas and severity, and may include:
- Topical creams for the affected area.
- Light therapy.
- In severe and advanced stages, methotrexate may be used.
- Therapeutic shampoo for psoriasis on the scalp.
How to Prevent Psoriasis?
There is no method to prevent psoriasis, but managing the disease can help improve symptoms and prevent exacerbations. Important ways to control psoriasis include:
- Recognizing and avoiding psoriasis triggers, such as:
- Skin injuries and sunburn.
- Infections, such as throat infections.
- Stress.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol. Forquitting smoking, here’s the guide..
- Climate factors like dry and cold weather.
- Some medications containing lithium, prednisone, and hydroxychloroquine.
- Maintaining a good skincare routine as per the dermatologist’s guidelines.
- Avoid scratching the affected area.
- Following a healthy lifestyle. For guidance on living ahealthy lifestyle, read this guide for you and life..
- Using medications when necessary.
- Ensuring sunprotection..
What Are the Complications of Psoriasis?
- Psoriatic arthritis.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis.
- Generalized pustular psoriasis.
When Should You See a Doctor?
- When symptoms occur and you need a diagnosis.
- In the case of generalized pustular psoriasis.
- In the case of erythrodermic psoriasis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Psoriasis Contagious?
No, psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease and cannot be transmitted through infection.